Modelado y clasificación de tráfico
La identificación de las aplicaciones que cursan sobre la red es fundamental para muchas tareas de administración y seguridad de la red. Existe una gran cantidad de enfoques en la literatura, la mayoría de los cuales se basan en comparación de patrones, técnicas estadísticas y aprendizaje automático. La aproximación más habitual y exitosa se basa en la identificación de patrones específicos de la aplicación en las cargas útiles transportadas. Esta aproximación, denominada de inspección profunda de paquetes (DPI) presenta problemas de eficiencia y privacidad y resulta inútil para el tráfico cifrado. Para proteger la privacidad del usuario, la mayoría de los métodos existentes se basan en atributos de tráfico en las capas de red y transporte, como esquemas de interacción, tamaños de paquetes y tiempos entre llegadas.
Nuestro interés reside en la clasificación de los flujos para la incorporación de esta información en los procesos de monitorización de la red y, especialmente, para su inclusión en los modelos de correlación para la detección de ataques multietapa. Nos centramos tanto en las técnicas DPI (los sistemas SIDS también aplican DPI) como en alternativas basadas en el análisis de los flujos sin inspección de sus contenidos, lo que es especialmente relevante en el caso de tráfico cifrado. También abordamos la clasificación en el caso de observaciones incompletas, esto es, en los casos en los que no es posible procesar todos los paquetes de un flujo.
Esta línea de investigación sirve de soporte actualmente a las dos líneas principales: seguridad en web y seguridad en IoT.
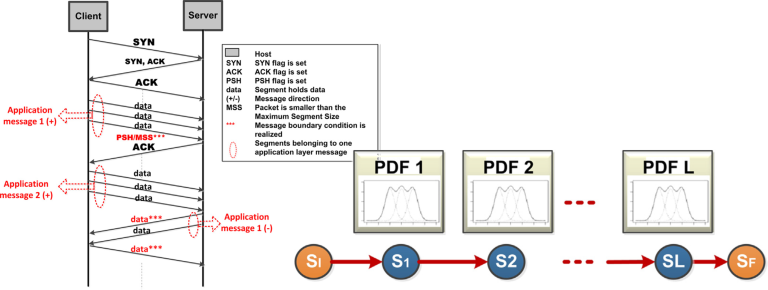
Destacan en esta línea el desarrollo de técnicas novedosas de identificación en base a los mensajes inciales de los flujos y técnicas que determinan los tipos de los flujos en base a interacciones entre nodos y/o relaciones temporales entre los flujos.
Líneas de trabajo
-
Identificación eficiente mediante análisis de cargas útiles en paquetes (DPI)
-
Identificación/clasificación de tráfico en base a parámetros de flujos y mensajes iniciales (clasificación temprana)
-
Análisis de secuencias de flujos para su clasificación
- Categorización de nodos por tipología de tráfico generado (interacciones entre nodos)
Técnicas / métodos
Aprendizaje automático
Análisis de series temporales
Comparación de patrones
Correlación de eventos
Resultados relevantes
Captura de tráfico en router acceso universidad (dataset privado)
ndpi_flowtools: Herramientas para identificación de flujos usando DPI y técnicas propias basadas en flujos
Publicaciones destacadas
Khalife, Jawad; Hajjar, Amjad; Díaz-Verdejo, Jesús
A sampling methodology for DPI classifiers Artículo de revista
En: Journal of Internet Technology, vol. 18, no 4, pp. 787–800, 2017, ISSN: 20794029.
@article{Khalife2017,
title = {A sampling methodology for DPI classifiers},
author = {Jawad Khalife and Amjad Hajjar and Jesús Díaz-Verdejo},
doi = {10.6138/JIT.2017.18.4.20130525},
issn = {20794029},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-01},
journal = {Journal of Internet Technology},
volume = {18},
number = {4},
pages = {787--800},
abstract = {In this paper we provide a general methodology for customizing sampling schemes used with DPI (Deep Packet inspection) based traffic classifiers. Sampling is supposed to optimize DPI classification by reducing the disclosed payload size for inspection and the associated computational overhead while providing better protection of the users' privacy. As a real case scenario, we choose a real traffic dataset captured on a campus network link on which we conduct a series of classification experiments joint with sampling using OpenDPI, as the DPI tool of choice. First, we attempt to statistically localize payload sections within a flow stream where application signatures are mostly matched by OpenDPI. Then, we specify the minimum required payload to be disclosed for inspection, on a per protocol basis. Finally, we recommend a methodology for generalizing one DPI sampling scheme.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Hajjar, Amjad; Khalife, Jawad; Díaz-Verdejo, Jesús
Network traffic application identification based on message size analysis Artículo de revista
En: Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 58, no 2010, pp. 130–143, 2015, ISSN: 1084-8045.
@article{Hajjar2015,
title = {Network traffic application identification based on message size analysis},
author = {Amjad Hajjar and Jawad Khalife and Jesús Díaz-Verdejo},
doi = {10.1016/J.JNCA.2015.10.003},
issn = {1084-8045},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-12-01},
journal = {Journal of Network and Computer Applications},
volume = {58},
number = {2010},
pages = {130--143},
publisher = {Academic Press},
abstract = {Identifying network applications is centric to many network management and security tasks. A large number of approaches exist in the literature, most of which are based on statistical and machine learning techniques. For protecting the user privacy, the majority of the existing methods rely on discriminative traffic attributes at the network and transport layers, such as interaction schemes, packet sizes and inter-arrival times. In this work, we propose a novel blind, quintuple centric approach by exploring traffic attributes at the application level without inspecting the payloads. The identification model is based on the analysis of the first application-layer messages in a flow (quintuple), based on their sizes, directions and positions in the flow. The underlying idea is that the first messages of a flow usually carry some application level signaling and data transfer units (command, request, response, etc.) that can be discriminative through their patterns of size and direction. A Gaussian mixture model is proposed to characterize the applications, based on a study of the common characteristics of application-level protocols. The blind classifier is based on Markov models with low complexity and reasonable computational requirements, where the training procedure consists of profiling the target applications separately. Promising results were obtained for some popular protocols including many peer-to-peer applications.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Khalife, Jawad; Hajjar, Amjad; Diaz-Verdejo, Jesus
A multilevel taxonomy and requirements for an optimal traffic- classification model Artículo de revista
En: International Journal of Network Management, vol. 24, no 2, pp. 101–120, 2014, ISSN: 10991190.
@article{Khalife2014,
title = {A multilevel taxonomy and requirements for an optimal traffic- classification model},
author = {Jawad Khalife and Amjad Hajjar and Jesus Diaz-Verdejo},
doi = {10.1002/nem.1855},
issn = {10991190},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
journal = {International Journal of Network Management},
volume = {24},
number = {2},
pages = {101--120},
abstract = {Identifying Internet traffic applications is essential for network security and management. The steady emergence of new Internet applications, together with the use of encryption and obfuscation techniques, ensures that traffic classification remains a hot research topic. Much research has been devoted to this topic by the research community in the last decade. However, an optimal traffic classification model has yet to be defined. Many techniques and formats have been described, with the current literature therefore lacking appropriate benchmarks expressed in a consistent terminology. Moreover, existing surveys are outdated and do not include many recent advances in the field. In this article, we present a systematic multilevel taxonomy that covers a broad range of existing and recently proposed methods, together with examples of vendor classification techniques. Our taxonomy assists in defining a consistent terminology. It could be useful in future benchmarking contexts by characterizing and comparing methods at three different levels. From this perspective, we describe key features and provide design hints for future classification models, while emphasizing the main requirements for promoting future research efforts. To motivate researchers and other interested parties, we collect and share data captured from real traffic, using two models to protect data privacy. Copyright textcopyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. With the huge amount of recently emergent papers in traffic classification, existing surveys cannot reflect current advances and trends in the field. In this article, we propose a multilevel taxonomy categorising and characterizing most existing methods at three different levels, which is vital for future benchmarks. We show comparisons, highlight on current research trends and describe the optimal future classifier's features. From the perspective of our taxonomy, we illuminate on research requirements both on the policy and technical levels. Copyright textcopyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Camacho, J.; Padilla, P.; García-Teodoro, P.; Díaz-Verdejo, J.
A generalizable dynamic flow pairing method for traffic classification Artículo de revista
En: Computer Networks, vol. 57, no 14, 2013, ISSN: 13891286.
@article{Camacho2013,
title = {A generalizable dynamic flow pairing method for traffic classification},
author = {J. Camacho and P. Padilla and P. García-Teodoro and J. Díaz-Verdejo},
doi = {10.1016/j.comnet.2013.06.006},
issn = {13891286},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
journal = {Computer Networks},
volume = {57},
number = {14},
abstract = {The goal of network traffic classification is to identify the protocols or types of protocols in the network traffic. In particular, the identification of network traffic with high resource consumption, such as peer-to-peer (P2P) traffic, represents a great concern for Internet Service Providers (ISP) and network managers. Most current flow-based classification approaches report high accuracy without paying attention to the generalization ability of the classifier. However, without this ability, a classifier may not be suitable for on-line classification. In this paper, a number of experiments on real traffic help to elucidate the reason for this lack of generalization. It is also shown that one way to attain the generalization ability is by using dynamic classifiers. From these results, a dynamic classification approach based on the pairing of flows according to a similarity criterion is proposed. The pairing method is not a classifier by itself. Rather, its goal is to determine in a fast way that two given flows are similar enough to conclude they correspond to the same protocol. Combining this method with a classifier, most of the flows do not need to be explicitly evaluated by the later, so that the computational overhead is reduced without a significant reduction in accuracy. In this paper, as a case study, we explore complementing the pairing method with payload inspection. In the experiments performed, the pairing approach generalizes well to traffic obtained in different conditions and scenarios than that used for calibration. Moreover, a high portion of the traffic unclassified by payload inspection is categorized with the pairing method. textcopyright 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Proyectos destacados
A-TIC-224-UGR20 – Modelado de Ataques y Detección de Incidentes de Ciberseguridad (MADINCI)
Entidad financiadora: Universidad de Granada – Junta de Andalucía – Proyectos I+D+i del Programa Operativo FEDER 2020
Entidad/es participantes: Univ. Granada y Univ. Sevilla – N. invest.: 6
Periodo: 01/01/2022 a 30/06/2023
@online{madinci,
title = {Modelado de Ataques y Detección de Incidentes de Ciberseguridad (MADINCI)},
url = {/neus-cslab/madinci},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
urldate = {2022-01-01},
issuetitle = {Proyectos I+D+i del Programa Operativo FEDER 2020},
number = {A-TIC-224-UGR20},
pages = {6},
institution = {Univ. Granada y Univ. Sevilla},
organization = {Universidad de Granada - Junta de Andalucía},
series = {01/01/2022 a 30/06/2023},
note = {20000 €},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
– Data exploration on a network security data
Entidad financiadora: Protectwise Inc.
Entidad/es participantes: Univ. Granada – N. invest.: 3
Periodo: 01/08/2014 a 31/10/2014
@online{protectwise,
title = {Data exploration on a network security data},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-01},
urldate = {2014-01-01},
pages = {3},
institution = {Univ. Granada},
organization = {Protectwise Inc.},
series = {01/08/2014 a 31/10/2014},
note = {11000 €},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
– Mejora de la gestión de red mediante análisis y caracterización del tráfico en redes corporativas
Entidad financiadora: SADESI (Junta de Andalucía)
Entidad/es participantes: Univ. Granada – N. invest.: 5
Periodo: 01/07/2010 a 30/06/2011
@online{sadesi,
title = {Mejora de la gestión de red mediante análisis y caracterización del tráfico en redes corporativas},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-01-01},
urldate = {2010-01-01},
pages = {5},
institution = {Univ. Granada},
organization = {SADESI (Junta de Andalucía)},
series = {01/07/2010 a 30/06/2011},
note = {25056 €},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {online}
}
